uld be peripheral vasodilation, hypotension and tachycardia; bradycardia could occur from parasympathetic (vagal) stimulation. Depressed level of consciousness, circulatory collapse and shock have been reported. If symptomatic hypotension should occur, supportive treatment should be instituted.
Valsartan is not removed from the plasma by hemodialysis.
Valsartan was without grossly observable adverse effects at single oral doses up to 2000 mg/kg in rats and up to 1000 mg/kg in marmosets, except for the salivation and diarrhea in the rat and vomiting in the marmoset at the highest dose (60 and 37 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis). (Calculations assume an oral dose of 320 mg/day and a 60-kg patient.)
11DESCRIPTION
Exforge is a fixed combination of amlodipine and valsartan.
Exforge contains the besylate salt of amlodipine, a dihydropyridine calcium-channel blocker (CCB). Amlodipine besylate is a white to pale yellow crystalline powder, slightly soluble in water and sparingly soluble in ethanol. Amlodipine besylate’s chemical name is 3-Ethyl-5-methyl(4RS)-2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate benzenesulphonate; its structural formula is
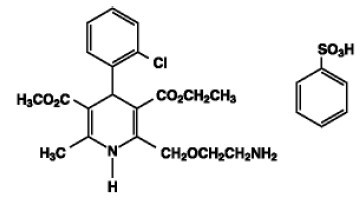
Its empirical formula is C20H25ClN2O5•C6H6O3S and its molecular weight is 567.1.
Valsartan is a nonpeptide, orally active, and specific angiotensin II antagonist acting on the AT1 receptor subtype. Valsartan is a white to practically white fine powder, soluble in ethanol and methanol and slightly soluble in water. Valsartan’s chemical name is N-(1-oxopentyl)-N-[[2’-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl) [1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-L-valine; its structural formula is

Its empirical formula is C24H29N5O3 and its molecular weight is 435.5.
Exforge tablets are formulated in four strengths for oral administration with a combination of amlodipine besylate, equivalent to 5 mg or 10 mg of amlodipine free-base, with 160 mg, or 320 mg of valsartan providing for the following available combinations:5/160 mg, 10/160 mg, 5/320 mg, and 10/320 mg.
The inactive ingredients for all strengths of the tablets are colloidal silicon dioxide,crospovidone, magnesium stearate and microcrystalline cellulose. Additionally the 5/320 mg and 10/320 mg strengths contain iron oxide yellow and sodium starch glycolate. The film coating contains hypromllose, iron oxides, polyethylene glycol, talc and titanium dioxide.
12CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Amlodipine
Amlodipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker that inhibits the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle. Experimental data suggest that amlodipine binds to both dihydropyridine and nondihydropyridine binding sites. The contractile processes of cardiac muscle and vascular smooth muscle are dependent upon the movement of extracellular calcium ions into these cells through specific ion channels. Amlodipine inhibits calcium ion influx across cell membranes selectively, with a greater effect on vascular smooth muscle cells than on cardiac muscle cells. Negative inotropic effects can be detected in vitro but such effects have not been seen in intact animals at therapeutic doses. Serum calcium concentration is not affected by amlodipine. Within the physiologic pH range, amlodipine is an ionized compound (pKa=8.6), and its kinetic interaction with t |



